Myth or Fact: Lithium-ion Batteries Self-Discharge After Being Fully Charged
Although ithium-ion batteries will discharge itself after being fully charged, it’s not as bad as you think. The rate of self-discharge is minimal and won’t pose any issues in real-world usage.
However, it is something that you need to keep in mind when storing the battery or during peak summer heat. If you’re new to the world of rechargeable batteries, then you might be surprised to hear that lithium-ion batteries self-discharge after being fully charged. This is not always a given with other battery types such as nickel cadmium (NiCd) or lead acid. In this article we’ll explore why this happens and what implications it has on how you use your battery.
What is Self-Discharge?
Why Does Self-Discharge Occur?
How long does it take a battery to self-discharge?
How fast do lithium batteries discharge?
How Does Self-Discharge Happen on Lithium-ion Batteries?
Ways to Deal with Lithium Battery Self Discharge
Actions to take for battery Self-discharge in Real Life Usage
How to Avoid Self-discharge When Fully Charged?
Is There Any Way to Stop Self-discharge from Happening?
Conclusion
What is Self-Discharge?
When the battery is in an open circuit state, the phenomenon of the stored power being consumed spontaneously is called the self-discharge of the battery, also known as the battery’s charge retention capacity.That is, under certain environmental conditions, the battery’s ability to store power is maintained.
In theory, the electrodes of the battery in the state of charge are in a thermodynamically unstable state, and physical or chemical reactions will spontaneously occur inside the battery, resulting in the loss of chemical energy of the battery.
Self-discharge is also one of the important parameters to measure battery performance. Different types of battery self-discharge factors and sizes are the same.The self-discharge rate of lithium batteries is slightly better than that of lead-acid batteries and significantly better than that of nickel-metal hydride batteries.
When a lithium-ion battery is not in use, it will lose some of its charge. This is known as self-discharge and it’s a natural process that occurs with all batteries. Study shows that batteries happens to discharge even faster when the battery isn’t being used properly or stored in suboptimal conditions.
Self-discharge has an impact on how you can use your battery and how long you can store it before it reaches the end of its useful life. The good news is there are some things you can do to slow down the self-discharge rate and get more out of your lithium ion battery, no matter how often you plan to use it. Here are the basics about Lithium Battery Self-discharge.
Want More Details: Download our battery design ebook.
Lithium Battery Design Design Ebook Download(2M, 20 pages, PDF)
Why Does Self-Discharge Occur?
1. Micro-short Circuit
Micro-short circuit is where a tiny electrical current leaks into the battery. The result is that the battery is damaged and stops working properly. This can happen if the battery gets wet, has electrolyte solvent or water in it, or if there are other small electrical components such as wiring that is touching it. It also happens when the battery is overcharged.

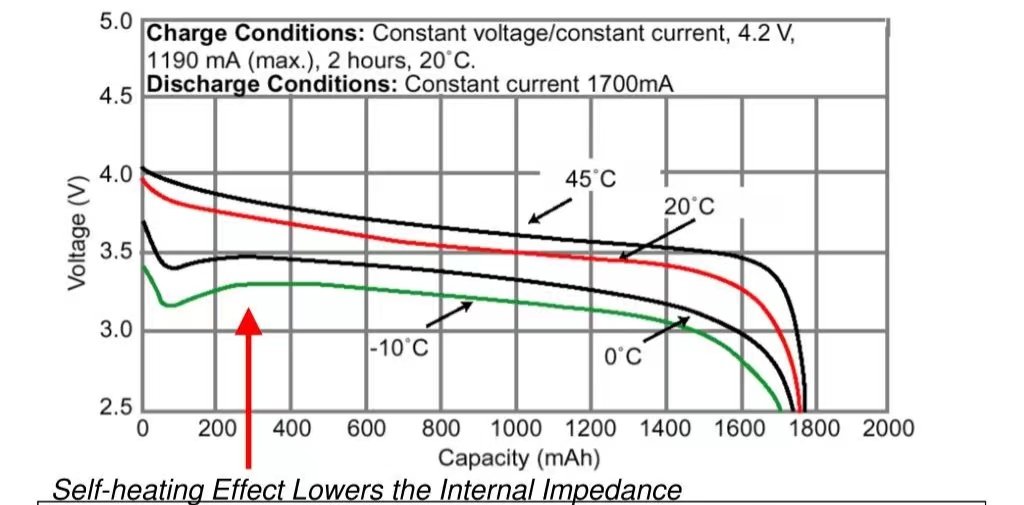
2. Temperature:
At high temperatures, the intensification of battery self-discharge can be summarized as the following reasons:
The stability of the SEI layer deteriorates and breaks, and regenerating the SEI consumes more lithium.
High temperature causes the positive electrode metal to dissolve faster;
Electrons are more active and easily participate in the side reactions of the negative electrode/electrolyte;
The activity of the electrolyte is enhanced, and the side reactions between the electrolyte and the electrode are intensified.
Temperature do impacts the self-discharge of lithium battery or lithium cell.
You can expect the self-discharge to typically double for every 10°¢ rise.
3. Electrolytic Solvents
Electrolytic solutions sometimes have high concentration of solvents and are used to speed up chemical reactions in labs. These solutions contain strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl) which may dissolve some non-polar solids like plastics, rubber and even glass which can lead to leakage from internal batteries of consumer electronics devices like cell phones, tablets and laptops.

4.Moisture
The most common cause of lithium battery self discharge is moisture. The electrolyte solvent or water in the battery get dissolved by the moisture, creating an imbalance in the electrolyte of the battery. When this happens, an electric short will be created and a lithium ion leak will occur, causing a fire.
SOC:
At the same temperature, the battery capacity under high SOC conditions decays faster. This is because under high SOC conditions, the negative electrode is in a lithium-rich state, which makes it easier to form an electron-ion-electrolyte complex, which exacerbates the reversible self-discharge of the battery.
How long does it take a battery to self-discharge?
What’s interesting about self-discharge is that it is non-linear with time. It means that a given battery’s self-discharge rate will change with the passage of time. The rate of self-discharge is also heavily dependent on temperature. The hotter a given battery is, the quicker it will self-discharge. Most lithium-ion batteries have a self-discharge rate of between 0.5-3% per month. This means that lithium battery will lose between 0.5 and 3% of its charge per month. At lower temperatures, this discharging rate will increase drasticaly.
How fast do lithium batteries discharge?
Lithium-ion batteries self-discharge at a rate of around 0.5-3% per month,depending on battery chemistry,enviroment,BMS etc. Strikingly, they discharge very fast while they are still fully charged. For a fully charged lithium battery or lithium cell, then it will lose 5-10% of its charge over the next month until it reaches 80% state of charge. under SOC of 30%-80%, the battery has most steady performance, around 0.5% or even less self discharging rate.
However, when you use a lithium-ion battery at low temperature or high temperature, it will discharge at a much higher rate. You can feel if your phone get hot, it dies quickly. like said previously,You can expect the self-discharge to typically double for every 10C rise.This is because a lithium-ion battery will fast discharge when it comes out of it’s best performing enviroment of 5-45°C degree. So, This means that if your device or battery temperature is too high or too low, the battery dies extremely fast.
How Does Self-Discharge Happen on Lithium-ion Batteries?
As we’ve seen above, lithium-ion batteries self-discharge even if they are fully charged. This means that they use up some of their charge even when they aren’t powering anything. If you fully charge a lithium-ion battery and then don’t use it, it will start losing charge.
This is due to the fact that the electrolyte inside a lithium-ion battery is made up of organic compounds. These compounds will break down over time when the battery is fully charged, and they will also break down when the battery is being charged.
This is why lithium-ion batteries are actually constructed with a voltage lower than the required cut-off voltage. This means that the battery will use up some of its charge below 3.6V and won’t break down due to overcharging.
Want More Details: Download our battery design ebook.
Lithium Battery Design Design Ebook Download(2M, 20 pages, PDF)
Ways to Deal with Lithium Battery Self Discharge
The best way to prolong lithium battery life is to store them in a cool, dry place. As a recommandation, 25 degree may best for lithium battery storage and least self discharge rate.
Higher temperatures and humidity levels will speed up the self-discharge, while lower ones will slow it down. Once you’ve used your lithium battery and charged it, don’t leave it plugged in.
Batteries left plugged in at all times will self-discharge much faster than if they’re unplugged. If you’re using your lithium battery in a device, make sure it’s fully charged before you put it away.
You can also prolong the life of your battery by using a low-voltage cut-off (LVC) feature. This will automatically shut off the battery when it’s at a certain level. Always use batteries that are equiped with good BMS design.
Finally, you should get your batteries tested at the one-year mark to make sure they still hold a charge. If they don’t, replace them before they become a fire hazard.
Actions to take for battery Self-discharge in Real Life Usage
Lithium-ion batteries self-discharge even when they are fully charged. This means that we, as consumers, will need to keep an eye on how long you leave a fully charged battery unconnected to anything.
There are two main things we may need to face of lithium-ion batteries self-discharging as consumers.
The first issue is with storing batteries for long periods of time. If you fully charge a lithium-ion battery and then don’t use it for a long time, it will lose its charge. This means that if you fully charge a lithium-ion battery and then don’t use it for 6 months or a year, it will lose a significant amount of charge.
Depending on the charging level of your battery when you put it away, it can lose a lot of charge. If you want to store a lithium-ion battery for a long period of time, then you should store it at a voltage below 3.6V. This will prevent the battery from losing too much charge.
The second issue with lithium-ion batteries self-discharging is with charging them. When you fully charge a lithium-ion battery, it will lose a certain amount of charge even while it is connected to the charger. The amount of charge that a battery loses while it is being charged by a charger is usually pretty low. However, it is something that you should keep in mind when charging your batteries.
How to Avoid Self-discharge When Fully Charged?
If you want to avoid your lithium-ion batteries self-discharging when fully charged, then you should avoid fully charging them. If you charge your batteries up to only 90-95% of their capacity, then they won’t self-discharge as much. This is because at this charge level, the batteries won’t break down as much due to overcharging. This is something you should keep in mind when charging your batteries.
However,
it is important to note that lithium-ion batteries self-discharge even when they are not fully charged. This means that it is better to charge your batteries to only 90-95% of their capacity instead of fully charging them and letting them self-discharge to 10%.
Is There Any Way to Stop Self-discharge from Happening?
The short answer is no.
Self-discharge is a natural process that happens in all types of rechargeable batteries. There is no way to stop it from happening.
However, there are some steps you can take to limit its impact. The first thing you can do is to charge your batteries to only 90-95% of their capacity. This will reduce the amount of self-discharge that happens while they are fully charged. Another thing you can do is to store your batteries at a voltage below 3.6V. This will prevent them from losing too much charge over time. You can also keep your batteries in a cool place like in your car’s glove box. Doing this will reduce the impact of self-discharge during the hot summer months.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries self-discharge after being fully charged, but it’s not as bad as you think. The rate of self-discharge is minimal and won’t pose any issues in real-world usage. You can slow down the self-discharge rate by charging your batteries to only 90-95% of their capacity. You should also protect your batteries from heat, because it will cause them to self-discharge faster. If you want to maximize the lifespan of your lithium-ion batteries.
Want More Details: Download our battery design ebook.
Lithium Battery Design Design Ebook Download(2M, 20 pages, PDF)
Prev Article: Basics on LiFePO4 Battery
Next Article: What You Need to Know About Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway









Hi, i read your articel about self discharge of li-ion batteries. What is the self discharge if i have a batterie on stock with a charge level of 3.6V
study show that lithium batteries will be discharged at about 3% self discharge rate per month.
You made an incorrect statement. Both lead-acid and NiCd batteries also self discharge. In the case of lead-acid, it is 1/2% per day.
Both
“The hotter a given battery is, the quicker it will self-discharge.”
and
“At lower temperatures, this discharging rate will increase drasticaly.”
within a single paragraph.
I suspect the first one is the one to keep in mind.
both are important reminders