All Things You Need to Know about NTC Thermistors
With the development of new energy, lithium batteries and lithium rechargeable batteries are widely used in automobiles, smart devices, and household appliances due to their excellent characteristics. Therefore, its safety and stability problem are of particular concern to people. As we all know, the failure of rechargeable batteries can lead to serious consequences, not only making the equipment itself unusable, but also may cause disasters such as explosions and fires, causing irreparable losses. Similar news is not uncommon. Therefore, it is very important to design an effective control strategy for rechargeable batteries (especially high-energy lithium-ion batteries), monitor the temperature changes of the battery in real time and react.
People can usually use some kind of temperature monitoring method to protect the battery, which requires a good design and suitable component specifications. And can follow up on temperature changes at any time and react quickly. The temperature sensor NTC thermistor is one of the simple and efficient semiconductor for monitoring temperature changes. Multi-specification, high-precision NTC thermistors can meet the different electrical and structural design requirements of engineers. It can detect temperature changes at all times and react quickly to protect the safe operation of the battery pack.
What is an NTC thermistor?
NTC stands for Negative Temperature Coefficient. NTC thermistors, as the name suggests, are resistors with negative temperature coefficient. This resistance changes with temperature. NTC is a negative temperature coefficient, and the resistance decreases with the rise of temperature, which is just the opposite of the positive temperature coefficient of PTC, which increases with the increase of temperature resistance.
PTC can be used in heaters and other products that require constant temperature, such as heaters. It can also be used in lithium battery over-current protection, etc. PTC has a corresponding PTC fuse, which is used for circuit over-current protection function.
The NTC thermistor has a large resistance in the cold state and a small resistance in the hot state. It is also made into a thermistor for detecting temperature. When the temperature rises, the resistance decreases. When the NTC thermistor reaches a threshold value based on the voltage in the circuit, it will trigger protective measures. Both NTC and PTC thermistors have corresponding thermistors, which are widely used in temperature detection applications.

Disadvantages of NTC Thermistors
NTC thermistors in series at the input terminal can play a role in suppressing excessive current, but NTC also has inherent disadvantages.
First of all, NTC is connected in series in a circuit. Although its resistance value will decrease and maintain a lower resistance value after normal operation, it will still cause the circuit voltage to drop. This has a negative impact on the efficiency of the power supply.
The other is that NTC has thermal inertia. When the charger is working normally, the temperature rises and heats up, and it is plugged back in immediately after unplugging. The NTC is not cooled, and it is still at high temperature, so it can’t suppress the current. At this time, the current will be very large, and the charger that does not usually have sparks will also have sparks.
Why are Lithium Batteries Equipped with NTC Thermistors?
Because the rechargeable battery may cause the battery temperature to be too high during the continuous cycle of charging and discharging, causing the original performance of the battery to degrade. NTC thermistors can play a role in temperature monitoring, control and compensation in suitable applications inside rechargeable battery packs.
The main functions of the NTC thermistor in the battery are as follows:
- The design cycle life of the battery can be guaranteed.
- The battery can be charged more cost-effectively.
- Accurate temperature measurement by thermistor is an important auxiliary element to display the remaining time of the battery.
Therefore, the use of thermistors in rechargeable batteries is to ensure that the battery maintains the best performance and safety, and to stably monitor the temperature of the rechargeable battery pack to protect your safety.
Classification of NTC
NTC thermistor is a kind of thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient, and its resistance value decreases with the increase of temperature. Since the change of resistance value varies according to the change of ambient temperature, it is often used as a temperature measurement, and its temperature measurement range is generally -10~+300℃. However, there are also thermistors that can measure higher temperatures. One of its more important parameters is the rated zero-power resistance value and accuracy, which is the resistance value at 25℃. We often say that the resistance value of the thermistor has actually defaulted to the resistance value at 25℃. The NTC thermistor is composed of poly-crystalline ceramics of mixed oxides. Different packaging applications of different materials are used in different occasions. NTC thermistors generally have three main functions: excessive current suppression, temperature measurement, and temperature compensation.
SMD Type NTC Thermistor
The most important advantage of SMD thermistors is their small size and no leads, which are very suitable for surface mount production.
Application:
- LCD
- Temperature compensation circuits for various instruments and equipment
- Battery temperature measurement
- Various microprocessors
- Chip temperature measurement, etc.

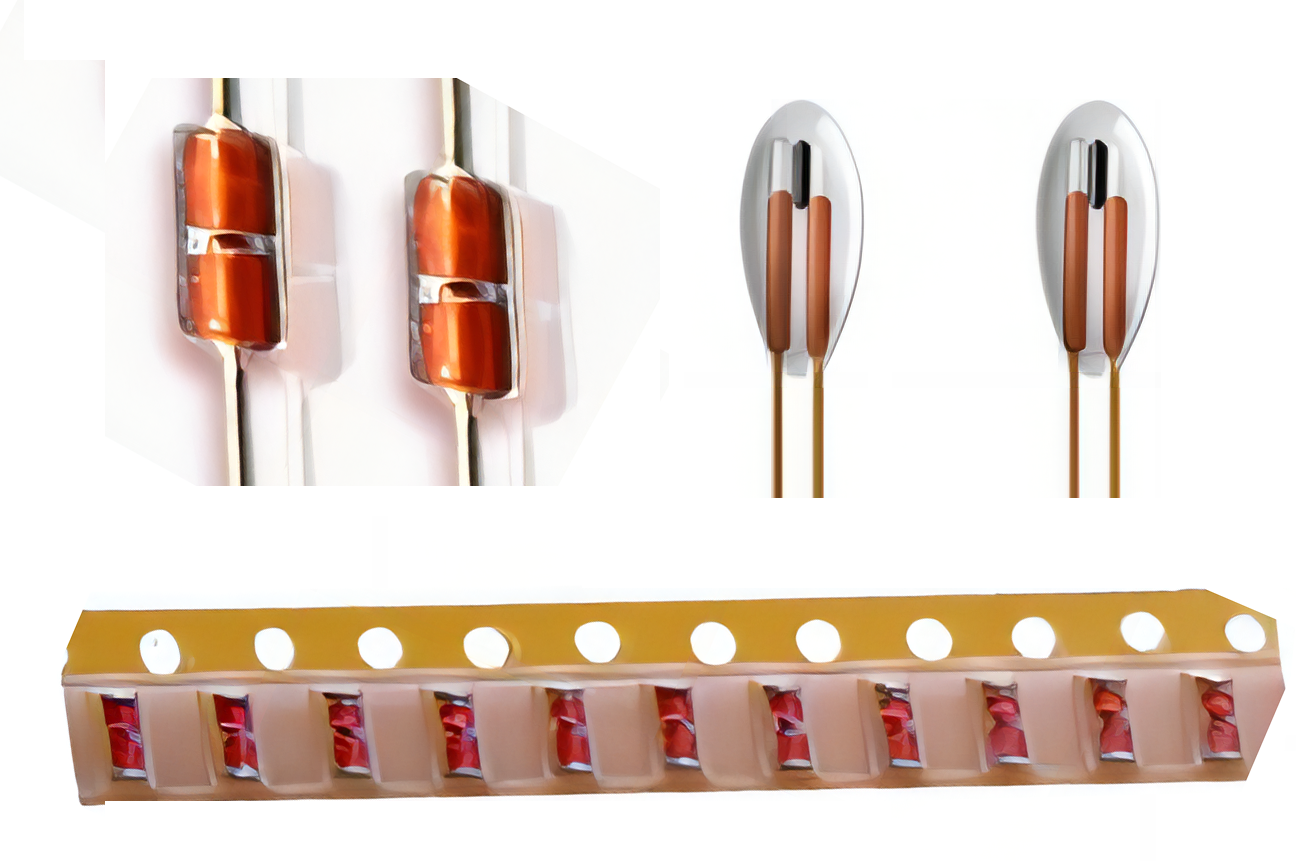
Glass-sealed NTC Thermistor
As the name suggests, it is a glass package with a thermal chip inside. There are generally three types of thermistors: SMD type, single-ended glass seal, and axial diode. If it is a plug-in and there are tinned pins, this kind of thermistor is very common. Many of us are basically exposed to this kind of thing.
Features:
- Small size
- Quick response
- High precision
- Anti-aging
- Because it is a glass package, it is more suitable for use in harsh environments such as high temperature and humidity.
Application:
- Various household appliances
- Temperature control and temperature detection of office automation equipment, etc.
Epoxy Package NTC Thermistor
This NTC thermistor chip is welded to various leads and encapsulated with epoxy resin.
The characteristics are:
- Smooth surface without burrs
- Black (or other colors) epoxy resin perfusion
- The resin is filled with fullness and no bubbles
- Small size
- Fast response speed
- High measurement accuracy, long-term stable work and good consistency.
Application: temperature measurement, control and compensation, high-precision instrumentation.


Small Head Diameter Enameled Wire NTC Thermistor
This kind of resistor is also packaged in epoxy, has a sturdy structure, and is a precision temperature sensor. There is a thermal insulation coating wire outside this resistor, also known as copper enameled wire. The existing conventional wire diameters are Ø0. 18mm, Ø0. 3mm and enameled wire with different wire diameters.
Application:
- 1.electronic thermometers
- 2.electronic desk calendars
- 3.mobile phone batteries
- 4.lithium-ion battery packs
- 5.various instruments and equipment that require different leads
Power Type NTC Thermistor
What we commonly use is in power supply products, mainly to suppress the excessive current generated at the moment of power-on. After the suppression of the excessive current is completed, the resistance value of the power-type NTC thermistor will drop to a very small extent, making the power consumption negligible.
Features:
- This kind of resistance material has a large constant B value
- Small residual resistance
- Long life
- High reliability
- Full series
- Wide working range
Application:
- Switching power supply
- UPS power supply
- Electronic energy-saving lamp
- Electronic ballasts and various other power supply circuits


Ceramic Body Ultra-high-power NTC Thermistor
Because it is packaged in a ceramic body, the material is high-purity, the process is more special, and the current resistance is stronger. Therefore, among the current family of power-type NTC thermistors, it is one of the strongest steady-state current thermistors with the strongest ability to suppress inrush current and work.
Therefore, it is particularly suitable for :
- Switching power supply
- UPS power supply
- Electronic energy-saving lamp
- Electronic ballasts and various other power supply circuits
Thin Film Type NTC Thermistor
This appearance is an insulating film type, which makes the thermal induction speed fast, high sensitivity, good stability, high reliability, small size, light weight, and easy to automate production. It is widely used in temperature measurement with a wide surface area, especially for small space applications, such as various communication products, electronic equipment, medical equipment, battery packs, and handheld instruments.
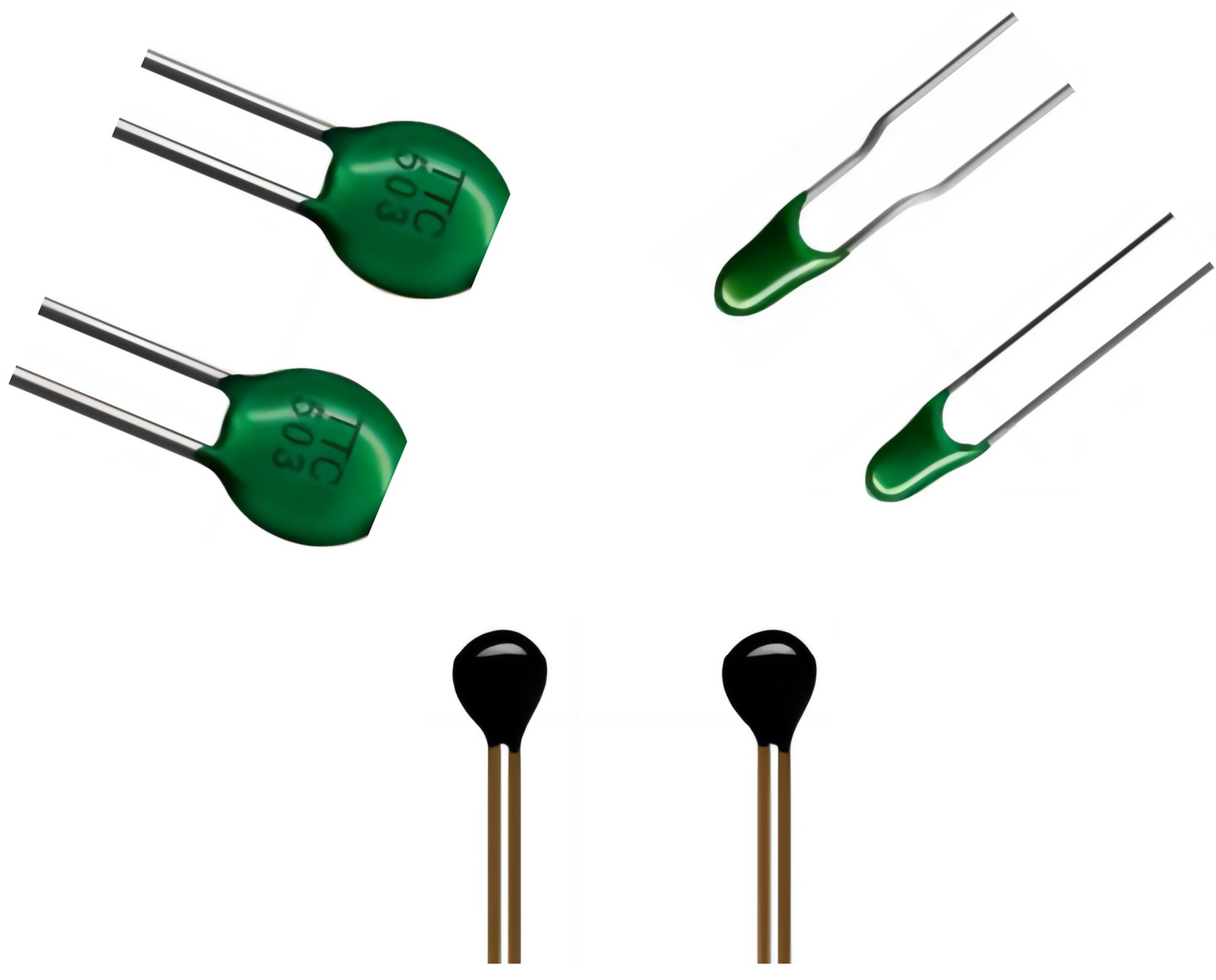


Compensated Thermistor
Many quartz oscillator circuits are internally equipped with temperature compensation circuits. Among them, compensated thermistors are used, but there are more chip-type resistors. As a compensation resistor, its production process is similar to that of other resistors, but it is more sensitive to temperature in terms of parameter requirements and the corresponding speed is faster.
Application: Transistor circuits and various compensation circuits.
Other Thermistor Components
The current development of NTC thermistors is not limited to separate types. Sometimes it is more combined with the sensor to form a variety of probe components, which are used as a whole sensor. At the same time, different packages are manufactured according to different occasions. For example, the use of double-layer sealing technology makes it more advantageous to resist mechanical collisions and bending while increasing insulation, and installation methods are also endless.
Application:
- Laser diode
- Optical components
- Industrial program control
- Car temperature measurement
- Aerospace, etc.

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
The Basic Characteristics of NTC Thermistors Include:
Zero power resistance value RT:
The DC resistance value of the thermistor gas measured at a specified temperature, if the temperature is not specifically specified, it is generally defined as 25℃. The change in resistance value caused by self-heating is negligible relative to the total measurement error. Generally, the zero-power measurement of the NTC thermistor is carried out in the thermostat, and there are two main factors that affect the total measurement error: one is the current through the NTC thermistor, and the other is the accuracy of the thermostat. There are many ways to reduce the current through the NTC thermistor. Once the current drops to a certain extent, it is often the accuracy of the thermostat that affects the measurement error.
B Constant:
The index of the sensitivity of the resistance value of the thermistor to temperature changes. The higher the sensitivity, the more sensitive the unit is K.
Heat Dissipation Coefficient:
The ratio between the change in dissipated power of the thermistor and the corresponding temperature appreciation, in mW/℃.
Thermal Time Constant:
The constant of the degree of reaction of the thermal performance of the thermistor, in seconds, generally rises from 25℃ to 85℃ and then drops.
Maximum Steady-state Current:
The maximum value at which the thermistor can continuously apply current.
Residual Resistance Value:
The resistance value when the maximum current is passed on the thermistor and it reaches a stable state. This is the scale consumed by the electrician when the thermistor is energized. Under the same maximum current, the smaller the value of the thermistor, the less power is consumed, and the less the temperature of the thermistor rises, the better the thermistor, in mW.
Maximum Allowable Capacitance:
The maximum allowable capacitance of a capacitor connected to a thermistor under load. Unit nF.
Prev Article: Will Sodium Batteries Replace Lithium Batteries?
Next Article: Lithium Batteries in Military



Leave A Comment